Cookies have been an integral part of the digital marketing landscape for over two decades. Third-party cookies in particular have enabled advertisers to track user behavior across websites and target ads based on their browsing history. However, increased privacy regulations like the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and privacy concerns have led to the demise of third-party cookies.
By the end of 2024, third-party cookies are being phased out by major browsers like Google Chrome. This marks a monumental shift for digital marketers who have heavily relied on third-party cookies to personalize marketing campaigns. With third-party cookies going away, businesses need to prepare for the cookieless future towards more privacy-centric strategies.
This transition will significantly impact digital advertising, analytics, and efforts to understand user behavior. Marketers must adapt to this new normal and find alternative solutions to targeting and tracking capabilities lost through cookies. While daunting initially, the cookieless future also presents opportunities to rebuild consumer trust and improve the digital experience.

Understanding Cookies and Their Impact
What Are Cookies?
Cookies are small text files that websites place on a user’s browser to store information about their activity across sites. There are two main types of cookies:
- First-party cookies – Set by the website domain the user is visiting directly. These are used to recognize repeat visitors, save shopping cart data, enable account logins, and provide a customized user experience.
- Third-party cookies – Set by external domains mainly for advertising purposes and cross-site tracking of user behavior. For instance, an ad placed on a website sets a third-party cookie to record user actions and target ads on other sites.
For digital marketers, third-party cookies have been the holy grail enabling targeted advertising and personalization for users. By following consumers across websites, marketers gained rich behavioral data to optimize campaigns. But these cookies also raised serious privacy issues by tracking users without consent.
The Controversy Surrounding Third-Party Cookies
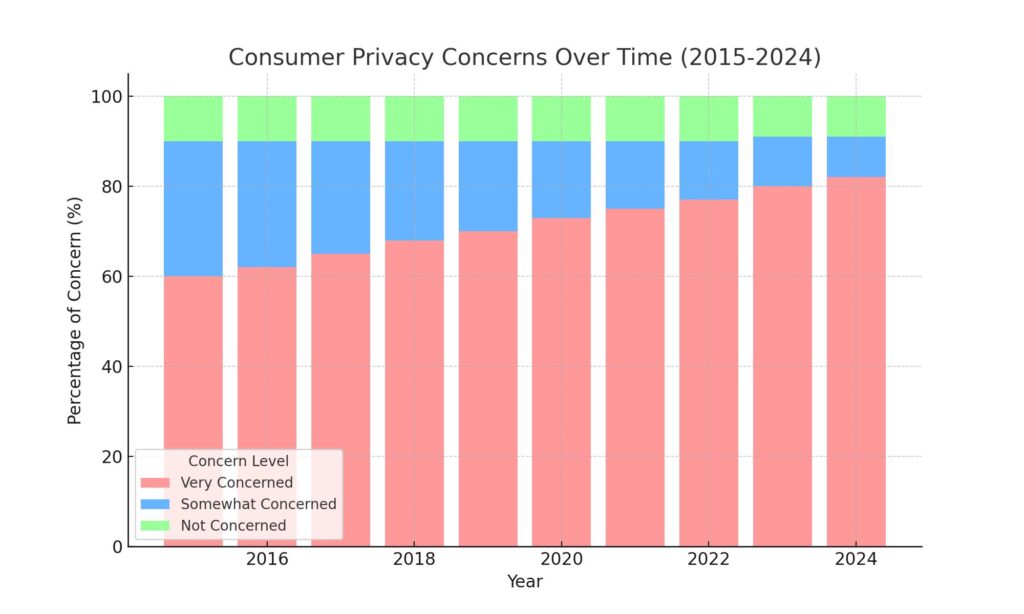
Third-party cookies have faced increasing backlash over privacy concerns, especially around sharing of personal data with unknown third parties. Major events contributing to the cookie controversy include:
- GDPR – The EU’s stringent 2018 data privacy law restricted use of cookies without explicit user consent. Violations risk heavy fines.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) – Similar to GDPR, the CCPA passed in 2020 gave California residents more control over their data.
- Browser crackdowns – Companies like Apple began blocking third-party cookies by default within Safari. Firefox also started restricting tracking cookies.
This hostile regulatory environment, coupled with shifting consumer attitudes to privacy, led Google Chrome to announce the phase-out of third-party cookies starting 2022, completing by Q2 2024. The demise of cookies will necessitate major changes in digital marketing.

The Implications of a Cookieless Future
For Consumers
For internet users, the cookieless future promises greater privacy and control of personal data. Third-party tracking of online activity without consent will no longer be possible. Targeted ads following users across the web will reduce.
However, consumers could also notice less personalized ad experiences. Retargeting based on browsing history will disappear. Contextual advertising and recommendations relying on cookies will diminish. The trade-off is enhanced data protection at the cost of relevant advertising.
For Marketers and Advertisers
The cookieless future leaves digital marketers without their most valuable targeting and analytics tools. Effective marketing strategies relying heavily on third-party data will need urgent reevaluation. Some major implications include:
- Limited consumer insights – Granular tracking of customer journeys, behaviors, and preferences will decline. Marketers lose visibility into conversion funnels.
- Reduced ad targeting capabilities – Retargeting campaigns based on browsing history will be impossible without cookies. Advertising personalization faces constraints.
- Decline in attribution modeling – Measuring the customer journey across devices and channels will be hindered without cross-site tracking.
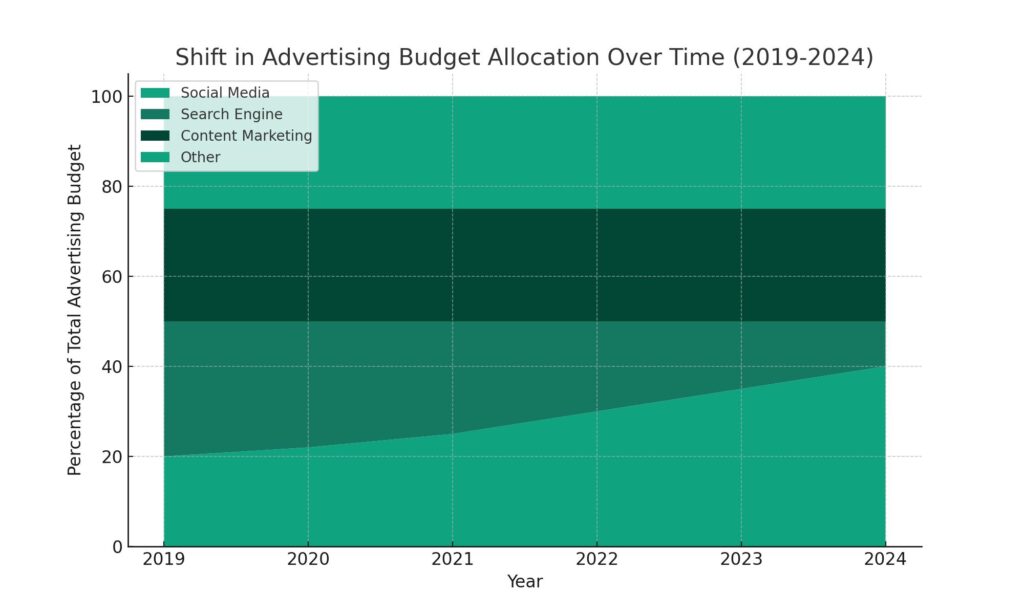
- Shift towards contextual methods – Marketers will increasingly rely on context like page content, searches, and keywords to target ads rather than past user actions.
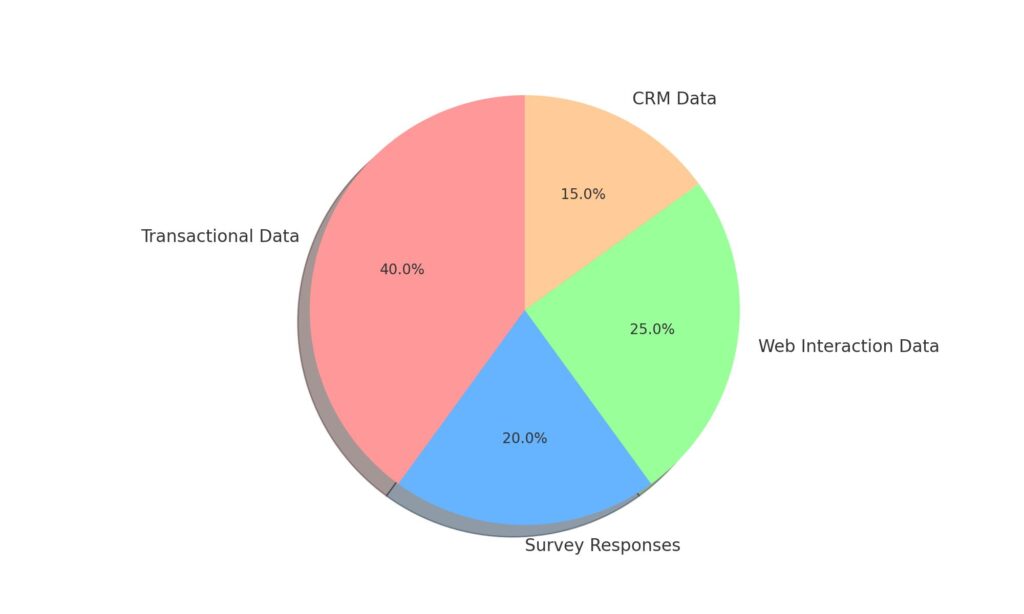
- Rise of first-party data – Customer data like emails and CRM information becomes more valuable for audience insights. Marketers must optimize first-party data collection and organization.
- Increased competition for walled gardens – Platforms with logged-in audiences like Facebook and Google hold advertising advantage in a cookieless world.
To navigate this future, marketing teams must adopt more privacy-centric strategies focused on first-party data, contextual targeting, and cross-device identity solutions. The companies best prepared for this cookie shakeup will gain a competitive edge.
Preparing for a Cookieless World
With the writing on the wall for cookies, forward-thinking marketers are already preparing for this new reality. Here are important steps to future-proof digital marketing in a post-cookie world.
Emphasizing First-Party Data
First-party data from owned marketing channels will be the most reliable for consumer targeting going forward. To reduce third-party cookie dependence, focus should shift to:
- Collecting zero-party data through surveys, feedback forms, and registrations to learn declared user preferences.
- Building robust CRM databases by incentivizing email sign-ups, app downloads, and purchases.
- Structuring first-party data for easy activation across channels like paid ads and site personalization.
- Identifying valuable metrics and KPIs beyond third-party cookies like engagement, conversions, LTV.
- Cleaning current data by deduplicating and removing obsolete information without third-party tracking.
Exploring Alternative Targeting Methods
While third-party cookies enabled granular individual-level targeting, marketers now need to explore alternatives like:
- Contextual advertising based on page content rather than user identity. Contextual data improves targeting, albeit less precisely than cookies.
| Contextual Targeting Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| Keyword analysis | Identify relevant keywords to target ads |
| Natural language processing | Analyze page semantics to match ad content |
| Site categorization | Target ads to specific channel or content types |
- Cohort analysis to identify common traits of valuable customer groups for lookalike targeting beyond individual tracking.
- Increased personalization across owned channels by applying first-party data and machine learning.
- Location data from consenting users adds physical context for proximity targeting.
- Publisher partnerships for data sharing and better audience segmentation.
Technological Innovations and Alternatives
Alongside strategy shifts, adopting emerging technologies can ease the cookieless transition:
Alternative Tracking and Targeting Methods
- Chrome Privacy Sandbox tools like FLoC enable interest-based targeting without individual profiles.
- Interoperable/universal IDs like Unified ID 2.0 offer anonymous targeted advertising when users log in to sites.
- PII-based solutions like email-based advertising enable deterministic matching without cookies.
- Browser fingerprinting uses device properties like OS and time zone to derive probable matches. However, fingerprints change and raise privacy concerns.
- Advanced contextual tools like GumGum‘s Verity and Google Topics use NLP and AI to classify content and match relevant ads.
- Differential privacy techniques allow collective insights from data without revealing individual user details.
Adapting to New Technologies
To fully leverage these emerging solutions, marketers should:
- Closely track development of Privacy Sandbox tools and early pilot opportunities.
- Evaluate identity resolution providers like LiveRamp to connect data across devices and environments.
- Assess customer data platforms (CDPs) to unify first-party data from all owned sources and activate across channels.
- Plan marketing technology stack upgrades like CRM and analytics to address changing requirements.
- Test up-and-coming contextual advertising tools to improve targeting without cookies.
Advantages of a Cookieless Future
Amidst the urgent preparations required, the cookieless future also presents some opportunities for digital marketing.
Benefits for Digital Marketing
- Enhanced brand safety as ads are less likely to appear next to questionable content without cookies.
- Reduced ad fraud with lesser anonymous traffic and bots.
- Improved campaign outcomes from better-quality context and first-party data.
- Cost savings from third-party data with focus shifting to owned assets.
- Faster page loads without excessive third-party tags and trackers.
Creating a More Trusting Consumer Relationship
- Showing respect for privacy builds consumer goodwill, loyalty and advocacy.
- Transparency about data practices differentiates brands as ethical and honest.
- Offering clear consent controls enables genuine opt-ins rather than implied consent.
- Prioritizing user experience over excessive targeting enhances engagement.
The cookieless future presents a chance to reset the advertiser-consumer relationship based on transparency and consent. Users reward brands that respect their privacy. Marketers must balance targeting needs with user-centric values.
Action Plan for Businesses
Ready, Set, Adapt!
Businesses preparing for the cookieless future should follow these steps:
Take stock of current strategy
- Quantify reliance on third-party cookies for targeting and attribution.
- Assess impact on existing tactics like retargeting when cookies disappear.
Build first-party data foundation
- Audit owned assets – website, mobile apps, newsletters, CRM.
- Identify untapped sources for zero-party data collection.
- Review consent practices and obtain explicit opt-ins if needed.
Explore alternate targeting approaches
- Test contextual methods on a small scale first.
- Evaluate emerging cross-device identity solutions.
- Consider changes needed in analytics methodology.
Upgrade technology stack
- Evaluate integration needs between martech tools.
- Ensure flexibility to incorporate new solutions.
- Plan for skills training on new platforms.
Define metrics and KPIs for cookieless success
- Determine goals, measurement and reporting in the new environment.
- Isolate impact of third-party cookies on current analytics.
Stay updated on Privacy Sandbox changes
- Follow announcements from Google and other browsers.
- Sign up for pilot programs to evaluate new tools.
- Share learnings and best practices with digital marketing team.
With proactive planning and testing, the cookieless transition can be smooth rather than disruptive. While third-party cookies served marketers well, their time is ending. The future offers new opportunities with creativity and consumer centricity.
Looking Beyond – The Future of Digital Marketing
Regulatory Response and Technological Shifts
Upcoming regulations will further limit third-party data usage:
- California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) – Strengthens data rights starting 2023.
- Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA) – Broad privacy law with 2023 enforcement.
- Colorado Privacy Act – Regulates use of sensitive data from 2023.
- Federal privacy law – Potential US nationwide regulations.
However, technology will also evolve with solutions like differential privacy and trusted web ecosystems. Advertising can remain viable in a privacy-first world.
Embracing New Opportunities
Despite current uncertainty, marketers should view the cookieless future with optimism.
- Data will hold more value when users intentionally share it.
- Strengthening first-party relationships builds loyalty beyond transactions.
- Constraints drive innovation – new ideas will enable effective advertising without third-party cookies.
- Ethical use of data and emerging technologies will triumph over unconsented surveillance marketing.
The cookieless future promises a new chapter where both consumers and businesses can thrive. With a collaborative mindset, privacy and personalization can coexist in a way that respects user rights. Marketers have the chance to lead the change towards an improved digital marketing landscape.
Conclusion
The third-party cookie has been the backbone enabling digital marketing growth for years. But with privacy concerns and regulatory actions, its days are now numbered. Browsers like Chrome plan to phase out third-party cookies by 2024.
This monumental shift will significantly impact how marketers track users, target ads, and personalize experiences. Reliance on third-party data will face challenges. However, alternatives like first-party data strategies, contextual advertising, and new technologies offer solutions to the cookieless transition.
With the right preparations focused on transparency, consent, and innovation, businesses can adapt to the new normal. Respecting user privacy while delivering relevant experiences will be critical. The cookieless future no doubt brings complexity, but also unique opportunities to transform digital marketing. By putting people first, marketers can pave the way for sustainable growth even without third-party cookies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the cookieless future?
The cookieless future refers to the gradual phase-out of third-party cookies, which have been the backbone of digital advertising. This shift is driven by growing consumer privacy concerns and regulatory actions, forcing marketers to find new ways to reach and engage their audiences.
Why are third-party cookies being phased out?
Third-party cookies have faced increasing scrutiny due to privacy concerns, as they allow cross-site tracking and data collection without user consent. Regulations like GDPR and CCPA have put pressure on tech companies to limit the use of these invasive tracking mechanisms.
How can marketers adapt to the cookieless future?
To adapt, marketers must emphasize first-party data collection, leverage contextual advertising, and explore emerging technologies like cohort analysis and privacy-preserving identifiers. Embracing a balanced approach that respects user privacy while delivering effective campaigns is key.
What are the benefits of a cookieless future for digital marketing?
The cookieless future can enhance brand safety, improve campaign outcomes, and lead to cost savings for businesses. It also presents an opportunity to build more trusting relationships with consumers by prioritizing privacy and transparency.
What alternative tracking methods are available in a cookieless world?
Alternatives include PII-based identifiers, browser fingerprinting, and Google’s Privacy Sandbox initiatives like Federated Learning of Cohorts (FLoC) and Topics API. Interoperable universal IDs are also being explored as privacy-centric solutions.
How can businesses prepare for the cookieless future?
Businesses should assess their current data and targeting strategies, enhance first-party data collection, explore alternative targeting approaches, stay informed about industry developments, and maintain a balanced approach between privacy and marketing needs.
What is the future outlook for digital marketing in a post-cookie era?
Regulatory changes and technological advancements will continue to shape the digital marketing landscape. Marketers must embrace innovation, collaborate, and focus on delivering value to customers while respecting their privacy preferences.
How will the cookieless future impact consumer experiences?
Consumers will likely experience increased privacy and data protection, but may also see changes in personalized and targeted advertising. Businesses must balance these considerations to build trust and maintain positive customer relationships.
What role do first-party data and contextual advertising play in the cookieless future?
First-party data and contextual advertising are becoming increasingly important as alternatives to third-party cookie-based targeting. Marketers must invest in strengthening their first-party data strategies and leveraging contextual insights to reach their audiences effectively.
How are tech companies responding to the cookieless transition?
Major tech companies, such as Google, are developing new solutions to address the challenges posed by the cookieless future. These include initiatives like Privacy Sandbox, which aims to provide privacy-preserving alternatives to third-party cookies.
